Azithromycine - Zithromax - Azyth - Azi-Once Analysis
Laboratory analysis of drugs to certify the presence and measure the quantity of Azithromycin.
The level of uncertainty of the Azithromycin content analysis depends on the declination selected (Standard <20%, Precise <10% or Regulatory <5%).
Follow the instructions to send your drug to our laboratory for analysis.
Results within 15 working days of receipt of sample.
Azithromycin is a popular broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Azithromycin is included in the World Health Organization's (WHO) list of essential medicines.
Azithromycin is the active ingredient in Zithromax, marketed by Pfizer.
Due to its popularity, Azithromycin is one of the most widely sold drugs on the Internet, and also one of the most counterfeited on the market.
Ordering drugs from dubious sites is a health risk. It is essential to check that the online pharmacy is serious and has all the necessary authorizations.
If you have any doubts about the origin of the drug, you should carry out an analysis to certify the presence of the active ingredient and check that its dosage in the drug complies with the indicated content.
Analysis
Azithromycin is analyzed by liquid chromatography coupled with UV-Visible spectrophotometric detection (HPLC-UV Visible).
Chemical name
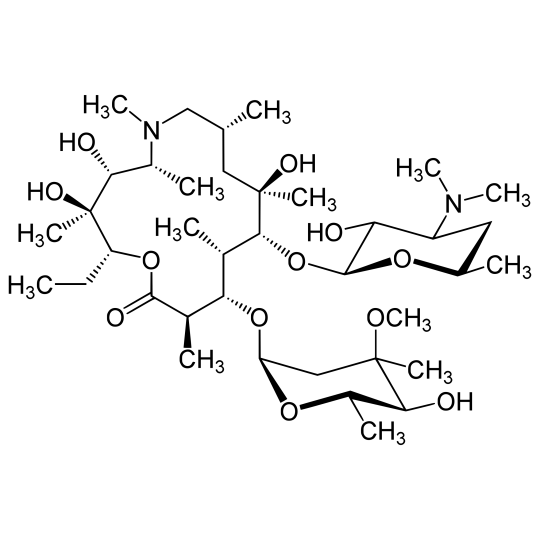
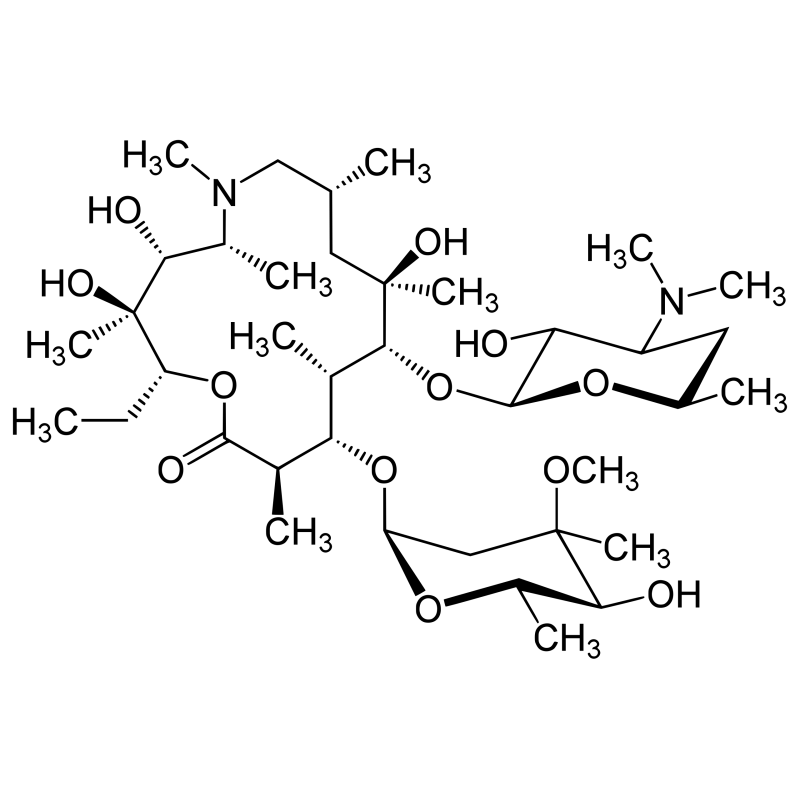
- Chemical name: (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13R,14R)-2-Ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-tridesoxy-3-(diméthylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one
- Chemical formula : C38H72N2O12
- CAS number : 83905-01-5
Therapeutic class
- Therapeutic class: Macrolide antibiotic
- Subclass: Macrolide azalides
Description of Therapeutic Effects
Azithromycin is an antibiotic used to treat various types of bacterial infections. It is effective against respiratory tract infections, skin infections, ear infections and certain sexually transmitted infections.
- Mechanism of action: Azithromycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, thus preventing bacterial growth. Its prolonged half-life means it can be administered less frequently, often just once a day for 3 to 5 days.
- Use: In addition to respiratory infections (pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis), azithromycin is often used to treat pharyngitis, bacterial meningitis, skin infections and early-stage Lyme disease. It is also indicated for sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia.
Trade names
Azithromycin is marketed under various brand names, the main ones being :
- Zithromax: The best-known brand name, manufactured by Pfizer
- Zmax: An extended-release formulation
- Azithromycin Sandoz: A generic version
- Sumamed: Used in some European countries
- Azyth: Another generic name
- Azi-Once: A generic brand used in several regions
Main Manufacturers
Several pharmaceutical companies produce azithromycin, including:
- Pfizer: The original manufacturer of Zithromax, which developed azithromycin.
- Sandoz (division of Novartis): Producer of generic versions of azithromycin.
- Teva Pharmaceuticals: A major manufacturer of generic azithromycin.
- Mylan: A major player in the production of generic versions, available in many countries.
- Cipla: Producer of generic versions of azithromycin, notably in Asia and Africa.
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries: Manufacturer of generic azithromycin for the global market.
- Hetero Drugs: An Indian pharmaceutical company producing generic azithromycin.
Precautions and side effects
- Precautions: Azithromycin should be used with caution in patients with a history of cardiac disorders (QT interval prolongation), liver disease or allergies to macrolides. Caution is also advised in case of interaction with other QT-prolonging drugs.
- Common side effects: Gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain), headaches, skin rashes, allergic reactions.
- Serious side effects: severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), heart rhythm disorders (QT interval prolongation), liver damage or acute pancreatitis.
Specific References
Your drug is analyzed by our expert pharmaceutical analysis laboratory.
The drug to be analyzed must be sent in at least 3 copies in its original packaging (box or vial + blister pack) in order to have all the information.
The drug to be analyzed must be sufficiently protected to avoid any deterioration or damage during transport.
The drug to be analyzed must be accompanied by the completed analysis form.
Documents to download:
The use of counterfeit or illegal medicines (without patent authorisation) presents a proven risk to patients' health:
- Absence of the active ingredient
- Under-dosage of the active ingredient
- Over-dosage of the active ingredient
- Toxic synthetic or degradation impurities
- Presence of another active ingredient
- Toxic excipients
- Presence of toxic residual solvents
- ...
The trade in counterfeit medicines is flourishing and growing exponentially with online trading. The authorities believe that more than half of all medicines sold over the Internet are counterfeit or illegal.